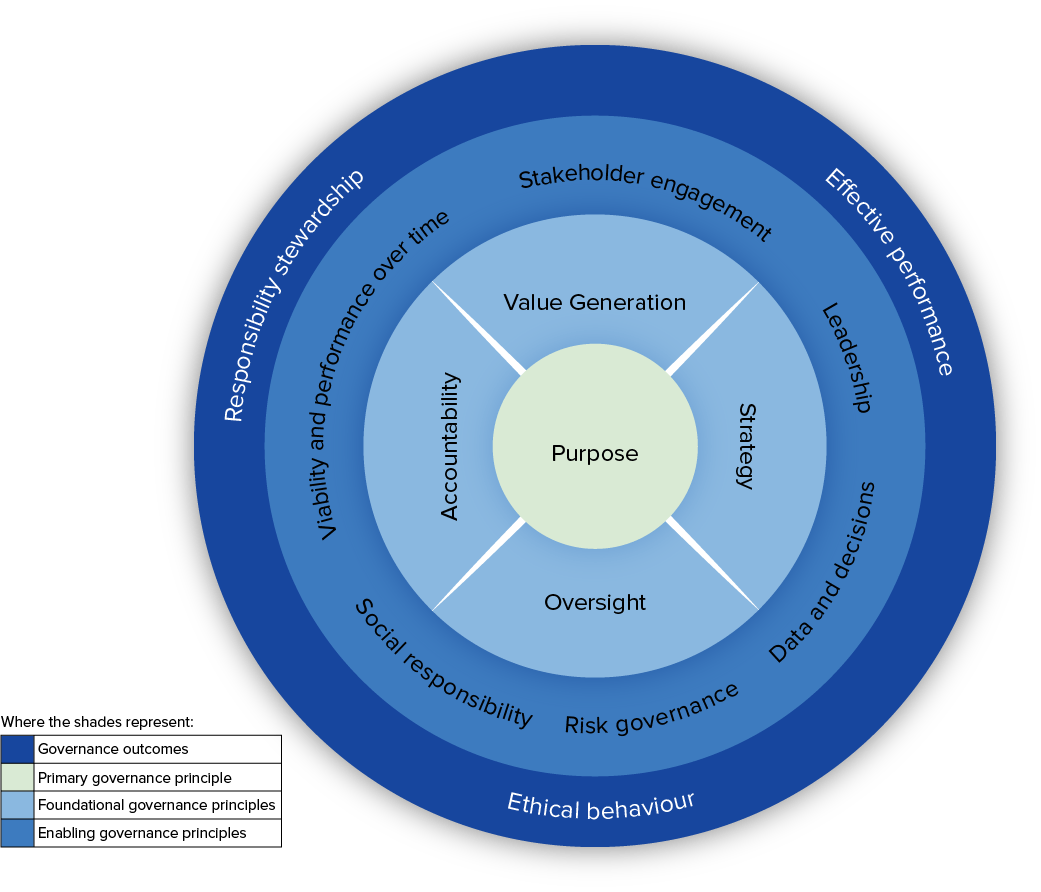
In today’s fast-changing and uncertain business world, corporate governance is no longer just a formality. Implementing good corporate governance has become an essential requirement for organizations seeking long-term success and sustainability.
However, many companies in Indonesia still view corporate governance as optional. In reality, sound governance practices serve as the foundation for building a resilient, transparent, and trustworthy organization.
According to The Indonesia Corporate Governance Manual, governance reforms are often applied only at the surface level. Many organizations treat them as tools for public image rather than as a genuine system to safeguard stakeholder trust, enhance access to capital, and minimize business risks. The real benefits of governance can only be realized when companies demonstrate a strong and continuous commitment to its implementation.
Why Corporate Governance Matters in Modern Business
1. Enhancing Investor and Stakeholder Trust
Transparent, accountable, and ethical corporate governance sends a strong signal to investors that the organization is well-managed. This builds a healthy investment climate, strengthens corporate reputation, and enhances public confidence.
2. Reducing Risks and Increasing Resilience
A strong governance structure enables companies to identify, mitigate, and respond to risks effectively — whether financial, operational, legal, or reputational. With solid governance in place, organizations are better protected from scandals, corruption, and compliance failures.
3. Supporting Better Decision-Making
Corporate governance provides a clear, data-driven decision-making framework. The principles of transparency, accountability, and responsibility guide executives and boards of directors in making fair and strategic decisions.
4. Driving Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Companies that take governance seriously tend to cultivate a healthy, adaptive culture that encourages innovation. This becomes a strategic advantage in navigating global competition.
Integrating Corporate Governance and IT Governance
Many leading companies have made good governance more than a regulatory obligation — they’ve embedded it into their organizational culture. Governance now extends beyond finance and compliance, encompassing how a company manages strategic risks and technological resources.
In the era of digital transformation, IT governance has become increasingly critical. It serves as an extension of corporate governance, ensuring that business strategies and IT capabilities remain aligned.
Through effective IT governance, organizations can ensure that their IT investments, data security, and digital services deliver measurable value and support strategic objectives. One of the most widely used frameworks to achieve this is COBIT.
COBIT: The Global Framework for IT Governance
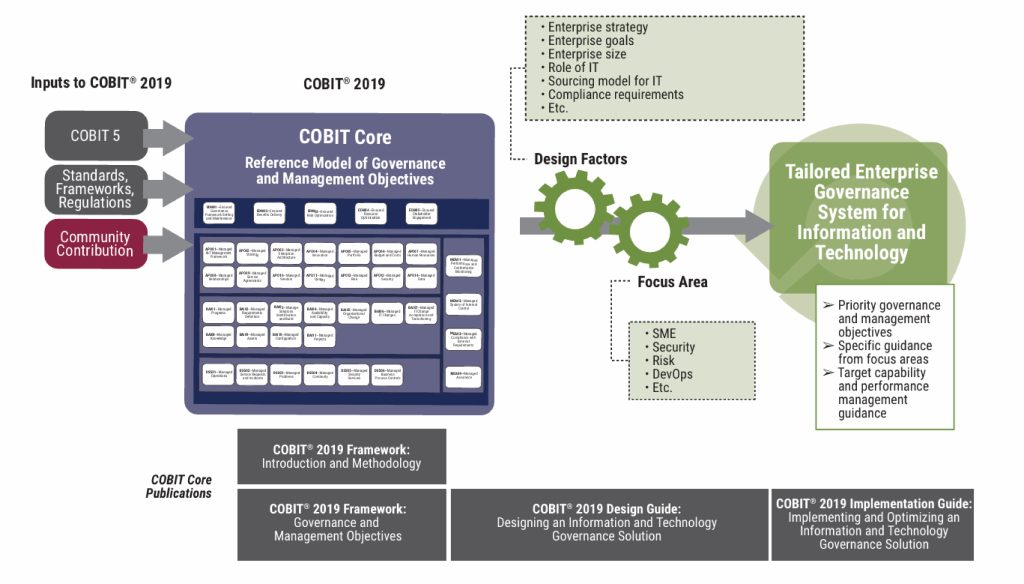
Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies (COBIT) is an internationally recognized framework developed by ISACA. Its latest version, COBIT 2019, offers a comprehensive and flexible approach to managing IT in order to:
-
maximize business value,
-
ensure effective risk management, and
-
strengthen compliance and sustainable performance.
COBIT 2019 provides a structured methodology that helps organizations tailor their IT governance according to business needs through design factors and focus areas.
The framework consists of four key publications:
-
COBIT 2019 Framework: Introduction and Methodology – introduces core concepts and principles.
-
COBIT 2019 Framework: Governance and Management Objectives – details 40 key governance and management objectives.
-
COBIT 2019 Design Guide – provides guidance for designing governance systems tailored to organizational context.
-
COBIT 2019 Implementation Guide – offers a roadmap for implementing and continuously optimizing IT governance.
Implementing COBIT has proven effective across various industries. For instance, a national bank in South Africa reported stronger IT governance and improved collaboration after adopting COBIT. Meanwhile, a customs organization in the Middle East experienced significant improvements in data reporting and operational efficiency following COBIT integration.
Partner with Robere & Associates
Robere & Associates Indonesia is ready to help your organization design, implement, and optimize IT Governance strategies effectively and sustainably.
Partner with us today and transform your governance into a powerful enabler of operational excellence and business growth. Contact Us !
 What Is the ISO 9000 Family?
What Is the ISO 9000 Family?